前言
異常是在程序執行過程中發生的意外情況,例如除以零、訪問 null 對象或遇到 file not found 錯誤。C#提供使用try、catch和finally塊處理的可靠機制。異常處理有助于處理在程序運行期間發生的任何意外或異常情況,異常是使用 throw 關鍵字創建而成。
正確管理異常是開發健壯的應用程序的一個關鍵方面。管理好異常的好壞意味著平穩運行的應用程序與故障排除的噩夢之間的區別。
在C#中引發異常的三種常見方法是throw、throw ex 和 throw new Exception(ex),盡管它們看起來很相似,但它們都有不同的行為和實例。本文探討它們的差異,并以示例介紹每種方法使用。
基礎知識
1、throw 語句
throw 語句用于指示異常的發生。用于顯式地引發異常或重新引發捕獲的異常。使用 throw 語句重新引發異常時,它會保留原始異常的堆棧跟蹤,這對于調試至關重要。
下面示例:throw 語句會重新引發捕獲的異常,同時保留原始堆棧跟蹤。
try{ //文件不存在 string content= File.ReadAllText(string.Format("{0}{1}log.txt",AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory,Path.DirectorySeparatorChar),Encoding.UTF8);}catch (Exception ex){ Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); throw;}
2、throw ex 語句
throw ex 語句是重新引發異常的另一種方法。但是,與 throw 不同的是,throw ex 會重置堆棧跟蹤信息。這意味著新的堆棧跟蹤從調用 throw ex 的點開始,丟失發生異常的原始上下文。
下面示例:throw ex 會重新引發捕獲的異常,但堆棧跟蹤將從 catch 塊開始,這可能會掩蓋異常的根本原因。
try
{ int firstnum = 1; int secondnum = 0; Console.WriteLine(firstnum / secondnum);}catch (Exception ex){ Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); throw ex;}
3、throw new Exception 語句
throw new Exception() 是將原始異常包裝在新異常中,提供額外的上下文,同時仍包含原始異常。
下面示例:將使用自定義消息創建新異常,并將原始異常作為內部異常傳遞。這提供了額外的上下文,同時保留原異常的詳細信息。
try{ // log.txt 文件不存在 string content= File.ReadAllText(string.Format("{0}{1}log.txt",AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory,Path.DirectorySeparatorChar),Encoding.UTF8);}catch (Exception ex){ Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); throw new Exception("【log.txt】文件不存", ex);}
三者區別
1、堆棧跟蹤
throw:保留原始堆棧跟蹤,提供有關異常來源的完整信息。
throw ex:重置堆棧跟蹤,這可能會使調試異常的根本原因發生改變。
throw new Exception:為新的異常消息提供其他上下文,同時將原始異常保留為內部異常。
2、應用場景
throw:需維護原始異常上下文和堆棧跟蹤時,使用該方法。
throw ex:該方法謹慎,如需使用,應在重新引發異常之前向異常添加其他信息。
throw new Exception:如果需要往異常添加更多上下文,同時保留原始異常詳細信息,使用該方式。
示例
1、使用 throw
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Text;
namespace Fountain.WinConsole.ExceptionDemo{ public class UserBiz { /// <summary> /// 登錄 /// </summary> public void Login() { try { UserDiz userDiz = new UserDiz(); userDiz.GetUserData(); } catch (Exception ex) { throw; } } }
public class UserDiz { /// <summary> /// 獲取用戶數據 /// </summary> public void GetUserData() { try { throw new InvalidOperationException("用戶或密碼不正確!"); } catch (Exception ex) { throw; } } }}
堆棧跟蹤將指向 GetUserData 中異常的原始來源,從而更容易調試。
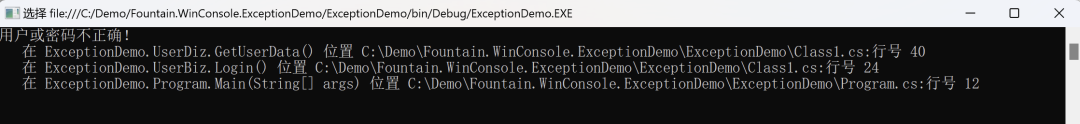
2、使用 throw ex
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Text;
namespace Fountain.WinConsole.ExceptionDemo{ public class UserBiz { /// <summary> /// 登錄 /// </summary> public void Login() { try { UserDiz userDiz = new UserDiz(); userDiz.GetUserData(); } catch (Exception ex) { throw ex; } } }
public class UserDiz { /// <summary> /// 獲取用戶數據 /// </summary> public void GetUserData() { try { throw new InvalidOperationException("用戶或密碼不正確!"); } catch (Exception ex) { throw ex; } } }}
堆棧跟蹤將僅顯示重新拋出點(Login),而不顯示異常的原始來源(GetUserData),從而更難確定錯誤最初發生的位置。

3、使用 throw new Exception
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Text;
namespace Fountain.WinConsole.ExceptionDemo{ public class UserBiz { /// <summary> /// 登錄 /// </summary> public void Login() { try { UserDiz userDiz = new UserDiz(); userDiz.GetUserData(); } catch (Exception ex) { throw new Exception("用戶登錄異常", ex); } } }
public class UserDiz { /// <summary> /// 獲取用戶數據 /// </summary> public void GetUserData() { try { throw new InvalidOperationException("用戶或密碼不正確!"); } catch (Exception ex) { throw new Exception("獲取用戶數據異常", ex); } } }}
新異常提供了額外的上下文,例如發生錯誤的方法名稱,同時仍保留原始異常詳細信息。
效果:
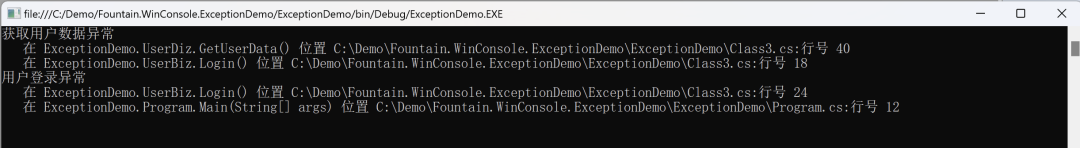
using System;
namespace Fountain.WinConsole.ExceptionDemo{ class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { try { UserBiz userBiz = new UserBiz(); userBiz.Login(); } catch(Exception ex) { if (ex.InnerException != null) { Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0}{1}{2}", ex.InnerException.Message, Environment.NewLine, ex.InnerException.StackTrace)); Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0}{1}{2}", ex.Message, Environment.NewLine, ex.StackTrace)); } else { Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0}{1}{2}", ex.Message, Environment.NewLine, ex.StackTrace)); } } Console.ReadKey(); } }}
小結
處理異常時,在throw、throw ex和throw new Exception 三者間進行選擇,對于有效處理異常和調試非常重要。從上面了解,throw 語句通常是首選,throw ex 需謹慎使用,對于throw new Exception則可用于復雜應用。
該文章在 2024/10/22 15:16:52 編輯過